13. Implementation of Banker's Algorithm in Operating System for deadlock avoidance
Banker's Algorithm is a resource allocation and deadlock avoidance algorithm used in operating systems to ensure that a computer system will not enter into a deadlock state. It simulates the allocation of predetermined resources to multiple processes in a way that avoids deadlock. The algorithm is named after the banking system, where the bank never allocates available cash in such a way that it can no longer satisfy the needs of all of its customers.
13.1. Concepts and Definitions
The Banker's Algorithm uses several data structures to keep track of the resources. The key concepts include:
- Available: A vector that indicates the number of available instances of each resource.
- Max: A matrix that represents the maximum demand of each process.
- Allocation: A matrix that represents the current allocation of each resource to each process.
- Need: A matrix indicating the remaining resource need of each process, which is calculated as Max - Allocation.
The algorithm proceeds by simulating each request and deciding whether it is safe to fulfill the request. A state is considered safe if there is at least one sequence of all processes in the system such that each process can request and obtain additional resources necessary to complete its designated task without causing a deadlock.
13.1.1. Algorithm of Banker's Algorithm
- Step 1: Initialize data structures to represent the number of available, allocated, maximum demand, and remaining need of resources for each process.
- Step 2: Find a sequence of processes where the remaining need of each process can be satisfied by the current available resources plus the resources held by all previously finished processes in the sequence.
- Step 3: If such a sequence exists, go to the next step. If no sequence is found, the system is in a deadlock state.
- Step 4: When a process requests a resource, determine if granting the request will leave the system in a safe state. A safe state is one where there exists a sequence that allows all processes to complete.
- Step 5: If the system remains in a safe state after the resource is allocated to the requesting process, grant the request. Otherwise, the process must wait for the resource.
- Step 6: Once a process has finished its job, it releases its resources and the available resources are updated.
- Step 7: Repeat the algorithm for each new resource request and release by the processes.
- Step 8: If all processes can be completed without any remaining unmet needs, then the system is in a safe state and free of deadlocks.
13.1.2. Implementation of Banker's Algorithm in C
The following C program demonstrates the implementation of the Banker's Algorithm. It assumes that there are a fixed number of resources and processes. Users will need to enter the maximum required resources, the allocation matrix, and the available resources at runtime.
#include <stdio.h>
#define P 5 // Number of processes
#define R 3 // Number of resources
// Function prototypes
void calculateNeed(int need[P][R], int max[P][R], int allot[P][R]);
int isSafe(int processes[], int avail[], int max[][R], int allot[][R]);
int main() {
int processes[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4};
// Available instances of resources
int avail[] = {3, 3, 2};
// Maximum R that can be allocated to processes
int max[P][R] = {
{7, 5, 3},
{3, 2, 2},
{9, 0, 2},
{2, 2, 2},
{4, 3, 3}
};
// Resources currently allocated to processes
int allot[P][R] = {
{0, 1, 0},
{2, 0, 0},
{3, 0, 2},
{2, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 2}
};
// Check system is in safe state or not
isSafe(processes, avail, max, allot);
return 0;
}
void calculateNeed(int need[P][R], int max[P][R], int allot[P][R]) {
for (int i = 0; i < P; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < R; j++)
need[i][j] = max[i][j] - allot[i][j];
}
int isSafe(int processes[], int avail[], int max[][R], int allot[][R]) {
int need[P][R];
calculateNeed(need, max, allot);
int finish[P] = {0};
int safeSeq[P];
int work[R];
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
work[i] = avail[i];
int count = 0;
while (count < P) {
int found = 0;
for (int p = 0; p < P; p++) {
if (!finish[p]) {
int j;
for (j = 0; j < R; j++)
if (need[p][j] > work[j])
break;
if (j == R) {
for (int k = 0; k < R; k++)
work[k] += allot[p][k];
safeSeq[count++] = p;
finish[p] = 1;
found = 1;
}
}
}
if (!found) {
printf("System is not in a safe state\n");
return 0;
}
}
printf("System is in a safe state.\nSafe sequence is: ");
for (int i = 0; i < P; i++)
printf("%d ",safeSeq[i]);
printf("\n");
return 1;
}This program will check for the safe state of the system after any resource request and prints a safe sequence if one exists.
13.1.3. Alternate Implementation of Banker's Algorithm in C
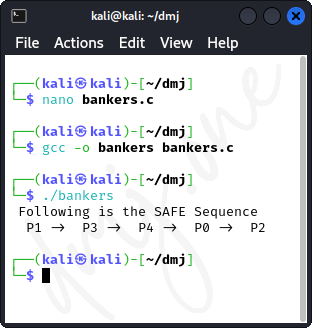
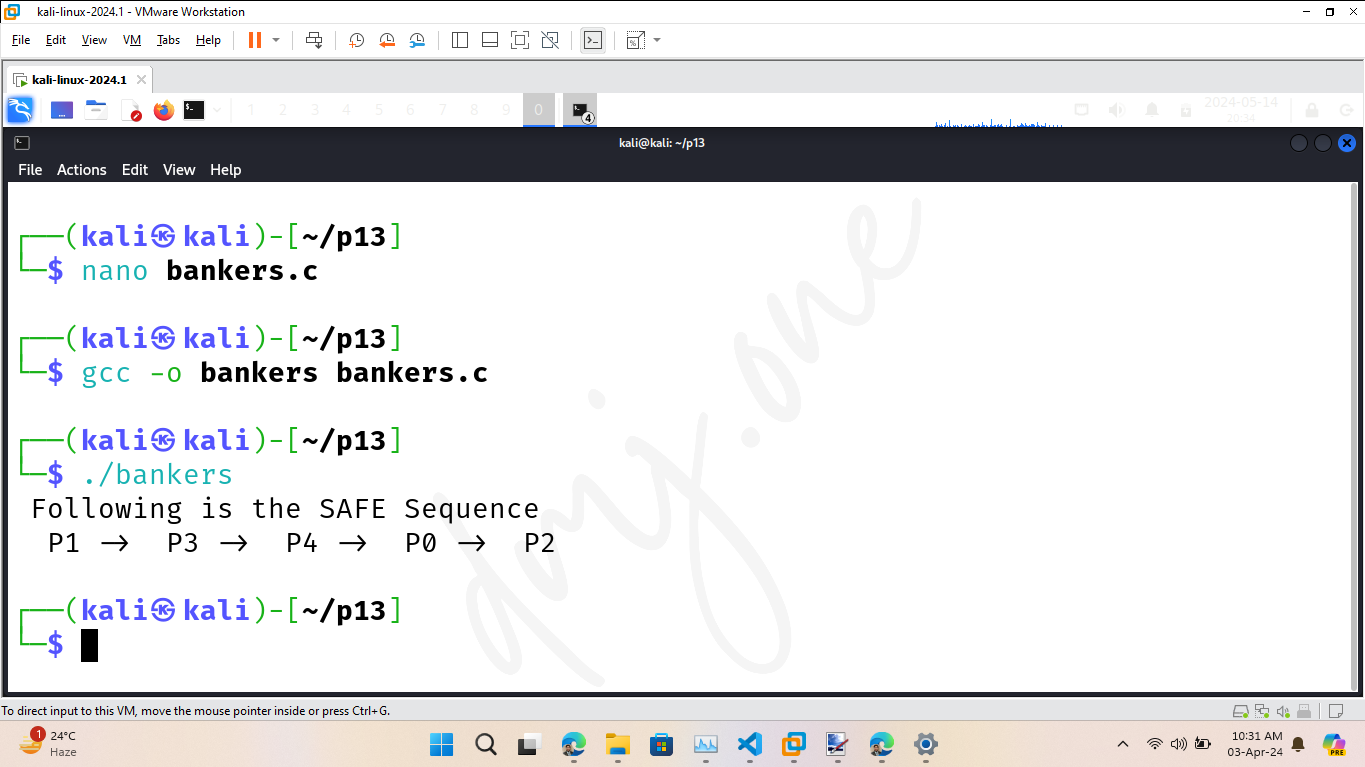
Below is an alternate implementation for the Banker's Algorithm in C.
// Banker's Algorithm
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// P0 , P1 , P2 , P3 , P4 are the Process names here
int n , m , i , j , k;
n = 5; // Number of processes
m = 3; // Number of resources
int alloc[ 5 ] [ 3 ] = { { 0 , 1 , 0 }, // P0 // Allocation Matrix
{ 2 , 0 , 0 } , // P1
{ 3 , 0 , 2 } , // P2
{ 2 , 1 , 1 } , // P3
{ 0 , 0 , 2 } } ; // P4
int max[ 5 ] [ 3 ] = { { 7 , 5 , 3 } , // P0 // MAX Matrix
{ 3 , 2 , 2 } , // P1
{ 9 , 0 , 2 } , // P2
{ 2 , 2 , 2 } , // P3
{ 4 , 3 , 3 } } ; // P4
int avail[3] = { 3 , 3 , 2 } ; // Available Resources
int f[n] , ans[n] , ind = 0 ;
for (k = 0; k < n; k++) {
f[k] = 0;
}
int need[n][m];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
need[i][j] = max[i][j] - alloc[i][j] ;
}
int y = 0;
for (k = 0; k < 5; k++){
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (f[i] == 0){
int flag = 0;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if(need[i][j] > avail[j]){
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if ( flag == 0 ) {
ans[ind++] = i;
for (y = 0; y < m; y++)
avail[y] += alloc[i][y] ;
f[i] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int flag = 1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(f[i] == 0)
{
flag = 0;
printf(" The following system is not safe ");
break;
}
}
if (flag == 1)
{
printf(" Following is the SAFE Sequence \ n ");
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
printf(" P%d -> " , ans[i]);
printf(" P%d ", ans[n - 1]);
}
return(0);
}